
Google is the biggest player among all search engines when it comes to searching information on the Internet. According to the estimates, over 3.5 billion searches are performed on Google Search every day. We (Google users) are only given a certain amount of information based on Google Analytics and Google Ads. Google uses its API
Table of Contents
- Why Do You Need To Scrape Google?
- Scraping Google Using Python InstallationImport LibrariesUse a KeywordBuild the Google URLGet the Results
- Installation
- Import Libraries
- Use a Keyword
- Build the Google URL
- Get the Results
- Use of Proxies
- Why Use Google Proxies?
- Conclusion
Google is the biggest player among all search engines when it comes to searching information on the Internet. According to the estimates, over 3.5 billion searches are performed on Google Search every day. We (Google users) are only given a certain amount of information based on Google Analytics and Google Ads. Google uses its API (Application Programming Interface) and essentially chooses the information most valuable for us based on its research and rankings. But what if we want to dig a bit deeper into what information is truly valuable to you?
Here comes the need for scraping. You can think of a Google scraper as a way to highlight the most important chapters of a book. When you scan a textbook for information, you tend to pick out the text that will be most valuable for your research or test. But the World Wide Web is larger than a 1000 page book. So, in the case of the Internet, Google scraper can be your laser-focused eye that immediately grabs and collects the top results on the topic you wonder about. You can extract Google search results based on specific keywords. For instance, if you scrape Google using the keyword “lions,” the Google web scraper will give you a certain number of top-rated URLs based on that keyword. The more keywords you use, Google will provide you with more specific URLs and data. The more specific the data, the more it will be tailored to your requirements. But let’s first understand the need to scrape Google.
Why Do You Need To Scrape Google?
You know that Google is the main entry point to the Internet for billions of people, and almost every business wants to appear in the Google Search results. Google ratings and reviews have a massive impact on the online profiles of local businesses. The marketing agencies having many clients from different industries rely heavily on obtaining reliable SEO (Search Engine Optimization) tools. They are a means to perform various tasks effectively and a means to manage and analyze the results successfully.
Following are some of the use cases of scraping Google.
- You can analyze ads for a given set of keywords.
- You can monitor your competition in both organic and paid results.
- You can build a URL list for specific keywords.

Businesses need to scrape Google for the following reasons.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) – Scraping Google shows a company how high their website page appears on the Google results page and gives a glimpse of how many keywords their website uses on any page. The more keywords a website uses, the higher that particular page appears on the result page. So, understanding how to utilize SEO keeps your business highly competitive.
- Marketing – The more we see the Amazon logo on our screens, the more likely we head to Amazon when we need to make a purchase. Google scraping helps collect data about how your competitors advertise their products, what products they choose to advertise, and how customers respond to those products.
- Competitive Sales Tactics – Google scraping helps your company create more competitive sales tactics. If your company ranks low on a particular results page, it might give insight into why a particular product of your company isn’t successful. Scraping gives you a leg up on your competition and offers new ways to be competitive in this world.
Scraping Google Using Python
Let’s see how we can scrape Google using python.
Installation
First, you need to install a fake-useragent. It grabs up-to-date useragent with a real-world database.
pip install fake-useragentImport Libraries
You have to import all the necessary libraries, as shown below.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import urllib
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
import requests
import re
from urllib.request import Request, urlopen
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupUse a Keyword
You have to build the Google URL using your keyword and the number of results. For doing this, we will follow the two steps:
Encode the keyword into HTML using urllibAdd the id to the URL
We suppose our keyword is “machine learning python.”
keyword= "machine learning python"
html_keyword= urllib.parse.quote_plus(keyword)
print(html_keyword)When we print out the keyword, we get the following result.
Build the Google URL
After encoding the keyword into HTML using urllib, we have to build the Google URL as shown below.
number_of_result = 15
google_url = "https://www.google.com/search?q=" + html_keyword + "&num=" + str(number_of_result)
print(google_url)We get the following URL:
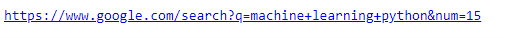
Get the Results
Now, we have to hit the URL and get the results. For achieving this, Beautiful Soup and Fake Useragent will help us with that.
ua = UserAgent()
response = requests.get(google_url, {"User-Agent": ua.random})
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")We only need the regular expressions to extract the information we want.
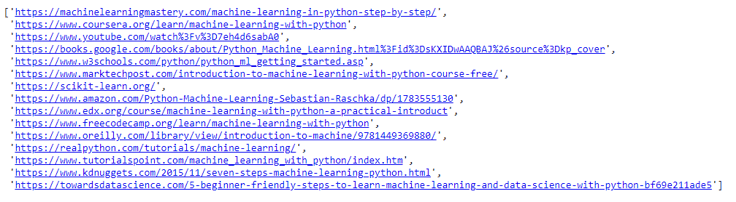
result = soup.find_all('div', attrs = {'class': 'ZINbbc'})
results=[re.search('\/url\?q\=(.*)\&sa',str(i.find('a', href = True)['href'])) for i in result if "url" in str(i)]
#this is because in rare cases we can't get the urls
links=[i.group(1) for i in results if i != None]
linksHere is what we get.
This is how you can scrape Google using Python.
We can also sum up the above code in a single scraper function, as shown below.
def google_results(keyword, n_results):
query = keyword
query = urllib.parse.quote_plus(query) # Format into URL encoding
number_result = n_results
ua = UserAgent()
google_url = "https://www.google.com/search?q=" + query + "&num=" + str(number_result)
response = requests.get(google_url, {"User-Agent": ua.random})
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
result = soup.find_all('div', attrs = {'class': 'ZINbbc'})
results=[re.search('\/url\?q\=(.*)\&sa',str(i.find('a', href = True)['href'])) for i in result if "url" in str(i)]
links=[i.group(1) for i in results if i != None]
return (links)Here google_results is our scraper function in which we pass the keyword and number of results as parameters and build the Google URL.
google_results('machine learning in python', 10)Here is what we get.

Use of Proxies
What if you want to connect to the Google Ads API? You can do this through a proxy by setting the http_proxy config in your google-ads.yaml file as shown below.
http_proxy: INSERT_PROXY_HEREYou can specify http://user:pass@localhost:8082 as a proxy. You can also configure the proxy setting programmatically with the help of GoogleAdsClient methods as:
- load_from_dict
- load_from_env
- load_from_string
For example,
config = {
...
"http_proxy": "INSERT_PROXY_HERE",
}
googleads_client = GoogleAdsClient.load_from_dict(config)You have to set the GOOGLE_ADS_HTTP_PROXY environment variable to use a proxy from load_from_env method.

Why Use Google Proxies?
The following are the reasons for using Google proxies.
- Get Fast and Unique Results – All search engines, including Google, frown upon using automated softwares to extract results. When they find several search inquiries coming from an IP address, they block the IP address and prevent it from getting access to any data. So, with a whole batch of unique and dedicated private proxies, not only will you be able to use the automated software for extracting the Google search results, but you will also be able to get the data extremely fast.
- Keep Privacy- Google proxies ensure that your original IP address will be safe and secure and will not be susceptible to any hacking attempts. They will also ensure that the sensitive information in your computer can be kept in a secure location.
- Automation – The automation software functions correctly using good quality proxies, and you do not need to purchase anything else in conjunction with having the dedicated proxies and automation software.

Conclusion
You can scrape Google using Python for:
- Competitor Analysis
- Building Links
- Highlighting Social Presence
- Searching Keywords
When scraping data from Google, proxies are essential as they can help companies boost their ranking on search engines and prevent their Internet IP from getting blocked. You can use a whole batch of dedicated proxies for scraping Google, and they help you get the data extremely fast.
Hope you got an understanding of how to scrape Google using Python.