Proxy vs. VPN: What Are The Differences And Which is Better?
When you hear the terms proxies and VPNs, it may often come to your mind that they are quite the same as they both mask your IP address. Both the tools indeed hide your IP address—however, the similarities stop right there. How differently they mask your IP address, along with the level of protection they
When you hear the terms proxies and VPNs, it may often come to your mind that they are quite the same as they both mask your IP address. Both the tools indeed hide your IP address—however, the similarities stop right there. How differently they mask your IP address, along with the level of protection they provide, and various other factors vastly differ.
So this article is for all the users out there who are eager to discover the differences between them.
What is a Proxy Server, and how does it work?
Let’s assume that you are a user in Seattle who wants to access a website with content restricted explicitly to the Spanish audience. This website would block any access to it from outside Spain. As a remedy, you can connect to a proxy server in Spain that would mask your location and use the proxy’s location instead, allowing you to access the content.
The proxy server acts as a middleman between you and the website, forwarding and requesting web traffic from the website. Therefore, the website does not know your presence, as it appears that all the requests are from the proxy server.
As you can see, the proxy server does not encrypt the data, and this poses security risks, particularly during the transmission of data on a public network. All it does is rerouting traffic between you and the source website at the application level.
Overview of different types of proxies
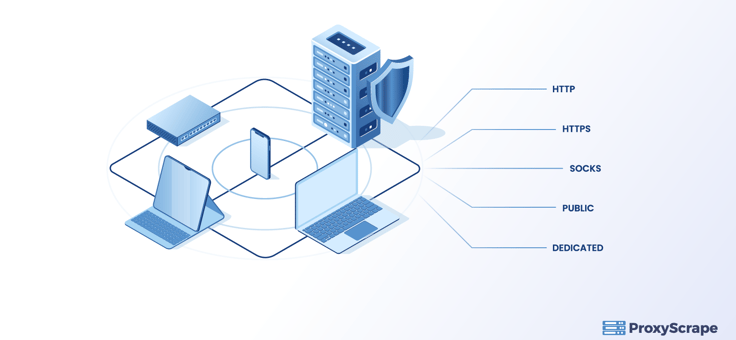
There are different types of proxy servers, such as HTTP proxies, Socks proxies, and dedicated. Proxies also can be classified into dedicated and public categories. Their functionality will depend upon the type that they belong to.
HTTP proxies – HTTP proxies request and forward web traffic by masking your IP address. They help you to access websites that are blocked by firewalls as well as geo-restricted websites. Since the HTTP proxies focus mainly on web traffic, they work at the application layer. They also cache any files or images, helping you to load the websites faster.
Socks proxies – Unlike the HTTP Protocols, the SOCKS proxies are not limited to web traffic, but they still work on the application layer. They are often used for connecting your client device to remote servers that require a UDP connection. You will have a greater level of anonymity.
Public proxies –Public proxies are freely available to any user. Since they are free, many people use them simultaneously, which causes ultra-slow speeds. There are other drawbacks as well, including security holes, misconfigurations, and lack of anonymity.
Dedicated proxies – With dedicated proxies, you pay for the IP, which is entirely dedicated for you. It lacks most of the drawbacks in public proxies. However, they can be more expensive as well.
Proxies can further be categorized as data center proxies and residential proxies. You can read more about different types of proxies here.
What is VPN, and how does it work?
As mentioned in the introduction, the mere similarity between a VPN (Virtual Private Network) and a proxy server is that they both conceal your IP address. However, unlike a proxy, a VPN also encrypts the data between you and the target website, ensuring complete protection from any malicious activity throughout the period that you are connected to it.
It achieves this higher level of encryption by building a tunnel from your device to the target device through the public network. This hides all your essential data until it reaches the destination.
Another fantastic benefit of VPN is that they work on the Operating System-level, implying that it will redirect all your traffic regardless of it coming from a web browser or any other background app.
Overview of different types of VPNs
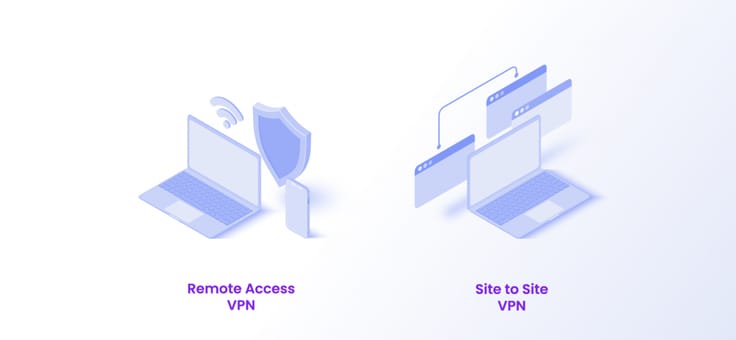
Just like with proxies, there are different types of VPNs categorized based on their functionality. There are two main types, and which one you use will depend on your situation.
Remote Access VPN
Remote Access VPNs enable you to connect to a private network within an organization and access its resources that the user is authorized to access. They are connected through the internet, and the encryption tunnel’s availability makes all communication between you and the private network secure. One of the most common examples is when you are on vacation on the beach; for instance, you will still access your company’s resources using a remote access VPN to download any files. Home users would also access the website’s content that is geographically restricted with a remote access VPN.
Site to Site VPN
Often large organizations use them with different branches in multiple locations, also known as Router-to-Router VPN. These VPNs enable the LAN (Local Area Network ) of one branch to be connected with the other branch’s LAN using the internet. Due to the strong encryption, the communication between the two networks is secure.
The site to Site VPNs function similarly to the client-server model. When one router of the network acts as the client, the other router acts as a server.
Key differences between VPNs and Proxies

By now, you must have realized proxies and VPNs are not quite the same, although they appear to be the same. This section will provide you with their critical differences between the two to avoid any further confusion that you may have.
Integration
Setting up proxies can be difficult because they are built to serve at the web application level. So ease of use with a user-friendly interface is not within the primary factors when designing proxies.
In contrast, VPN installation is just a few clicks away with simple instructions. Since the intended audience for VPN is pretty much a single user and operates at the OS level, its UI is more user-friendly. Therefore ease of use is a priority when designing VPNs.
Security
A VPN encrypts the data before it sends to the target device. Then after the data has reached the target device, the VPN will decrypt the data. Therefore this encryption mechanism ensures that your data will be safe and ideal for transferring sensitive information such as bank account or credit card information.
Free or public proxy servers will not perform any encryption on your data, so they are more likely to be intercepted by hackers. Unfortunately, this doesn’t get any better with paid proxy servers as they are limited in encryption ability.
Speed
The speed of the public proxy servers is extremely slow because many people use them concurrently. With dedicated proxies, the speed will depend on the server’s speed, which can go up to 1000MBs in most cases.
Although a VPN may confront a few milliseconds of latency due to its encryption algorithm’s employment, it is quite negligible. VPN can transfer data at a much faster rate from 50 Mbps upwards.
Cost
VPNs are more expensive than proxies due to the encryption mechanism being ingrained in them. While there are free VPNs out there in the market, you should not rely on them. As with any free service, there is a price that you have to pay.
In comparison, proxies can be freely available in the market, but as discussed numerous times, they are not reliable. Paid proxies are relatively inexpensive compared to VPNs.
Cookies
These days the cookies are present literally in every website that you visit. They pose a vulnerability to your online privacy. However, with a VPN, the cookie will store the VPN’s IP address mistakenly for yours, offering some protection from online theft. A proxy server will do likewise.
The next time you connect via a VPN or a Proxy, you need to clear all the cookies from the browser. Failure to do so will potentially result in you still being tracked even though you are using a proxy or VPN.
Benefits of using a VPN
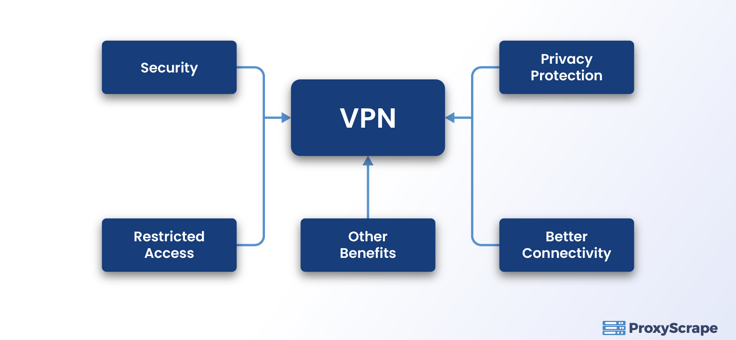
To sum up the benefits, it offers enhanced security due to the end-to-end encryption that it provides. Therefore you would be able to transfer sensitive information as usernames and passwords with ease.
VPNs protect your privacy up to a greater extent. Due to efficient encryption methods, you do not have to worry when your data transfers through public WiFi.
As you know, there is strong censorship of website content in certain countries, meaning governments and people try to control what you access. But you can take control of your hands with a VPN as they can bypass the restricted content.
Throughout the period that you connect to the internet using a VPN, your entire device will remain safe and anonymous.
Drawbacks of VPN
Unlike the proxies, most VPNs are not free, at least if you expect a reliable service.
Governments of some countries entirely ban VPNs. This is because they don’t want their citizens to access certain content that may deem immoral to that country’s cultural values. First of all, you need to check if VPNs are banned in your country to avoid landing in jail or paying hefty fines.
VPNs may cause performance issues as you have to connect your network to VPN before accessing the website. This will result in some considerable network delays.
When to use a VPN Server
With your knowledge gained so far, let’s dive into when to use a VPN. From the benefits and drawback, you may have discovered that VPNs are ideal for the following scenarios:
- When you have to send sensitive information across a public network or public WiFi.
- When you are worried that your information is likely to be prone to malicious acts by intruders.
- When you are unable to access certain content censored by the government of the country that you reside in.
- To protect you from Insider Threats.
Benefits of using a Proxy
There are numerous free proxies out there. So if you are on a low budget, this is your ideal option. It helps to mask your IP address by acting as a middle man. You can access the geo-targeted websites with block content. It caches your data so that it speeds up the connection speed to a particular web server.
Drawbacks of a Proxy server
Since your data is not encrypted, just like with a VPN, you never know when hackers or intruders steal your data. Unlike the VPN, proxies only work at the application level. So, therefore, it does not protect your entire system. As discussed in the advantage section, since proxies cache your data files, a proxy service provider can monitor your confidential information. Finally, when you are using a non-encrypted connection, the proxy server can modify the responses you get from the target website.
When to use a Proxy Server
To sum up, below are the ideal situations that you would consider using a proxy:
- When you would want to access content that is restricted in your country.
- When you want to watch a YouTube video or a blog post by being anonymous.
- To scrape or mine the content from popular websites.
- When your parents or employer is keen on monitoring your web activities.
Is there an advantage of using both a proxy server and a VPN?

It generally boils down to the point of what your goals are. If, for instance, you want to be anonymous for the entire duration of your web browsing, then the answer is a clear no. It’s also important to remember that VPN settings will override your proxy settings. So often, there is no point in using both. So I would say proxies (mainly residential proxies) are enough for most of the anonymous work you want to do on the internet.
Conclusion on Proxies vs VPNs
Now you may certainly have grasped the differences between Proxies and VPN. You have to decide which tool to use over the other, depending on the situation. You have to factor in security concerns, performance, geo-targeted content, and many other factors you have learned in this article. I hope you will take the right decision on when to use one over the other.