Behind Google, YouTube is the second most popular engine in the world. It is a video-sharing service where users can watch, share, like, comment, and upload videos. It is home to vloggers, informative content, educational videos, and lots of other data. Some of the main functions of Youtube are: With the help of web scraping
Behind Google, YouTube is the second most popular engine in the world. It is a video-sharing service where users can watch, share, like, comment, and upload videos. It is home to vloggers, informative content, educational videos, and lots of other data. Some of the main functions of Youtube are:
- Searching for and watching videos
- Creating a personal Youtube channel
- Uploading videos to your channel
- Subscribing other channels and users
- Liking and sharing other Youtube videos
- Creating playlists to organize videos together
With the help of web scraping, you can extract data from Youtube and benefit your organization by yielding valuable insights from that data. When you learn to extract data from Youtube, it is important to know what type of data you want. For instance, if you want to know peoples’ responses to your work, you can scrape the comments section for user sentiment analysis. Similarly, if you want to track the success of a video, you can scrape video performance data.
Before we learn how to scrape Youtube videos, let’s learn why we need to scrape them.
Table of Contents
- Why Scrape Videos On Youtube?
- Scraping Youtube Videos Using Python
- Setting Up The Python Environment
- Scraping Youtube Videos
- Import Libraries
- Setting Up the Driver
- Fetching the Youtube Video Links
- Create a DataFrame
- Using a Proxy to Scrape Youtube Videos
- Why Use Proxies For Scraping Youtube?
- Which Is the Best Proxy to Scrape YouTube Videos?
- FAQs:
- Final Thoughts on Scraping YouTube Videos Using Python:
Why Scrape Videos On Youtube?
Below mentioned are two main reasons for scraping Youtube data.
- Video Performance Data – When you post informational videos for a brand, it is important to track how your audience responds to them. Scraping the page for a specific video will help you receive the number of views, likes, dislikes, comments, channel subscribers, and more. You need to keep in mind the ratio of each of these metrics. For instance, a video can have millions of views and have more dislikes than likes. The number of views is not indicative of a well-liked or high-quality video. Instead, the ratio of views to likes/dislikes can be a form of sentiment analysis.
- Channel Data – When scraping the page for a Youtube channel, you’ll get data related to the playlists, number of videos, subscribers, and more. Further, scraping the pages of competing channels is useful and informative to understand better whether your channel is at the same level of influence as theirs.
- Achieve Automation – Robust web scrapers automatically allow you to extract data from Youtube. It saves time as you can collect data at greater volume than a human can ever hope to achieve.
- Business Intelligence and Insights – You can get a better picture of your competitors’ activity by downloading, cleaning, and analyzing data at significant volumes, leading to better business decision-making.
Scraping Youtube Videos Using Python
Let’s see how to extract Youtube video data using Selenium and Python. Selenium is a popular tool to automate web browsers. You can easily program a Python script for automating a web browser using Selenium.

Selenium requires a driver to interface with your chosen browser. For instance, Chrome requires a ChromeDriver that needs to be installed before you start scraping.
Setting Up The Python Environment
Step 1 – You need to open your terminal and install Selenium by using the command below.
$ pip install seleniumStep 2 – You need to download the Chrome WebDriver following the steps below.
- You have to visit https://sites.google.com/a/chromium.org/chromedriver/download.
- You have to select the compatible driver for your Chrome version.
- You need to check the Chrome version you are using by clicking on the three vertical dots in the top right corner.
- Then, you have to go to Help -> About Google Chrome.
Step 3 – You need to move the driver file to a PATH.
You have to go to the downloads directory and do the following.
- Unzip the file.
- Move it to usr/local/bin PATH.
$ cd Downloads
$ unzip chromedriver_linux64.zip
$ mv chromedriver /usr/local/bin/Scraping Youtube Videos
We will scrape the video ID, title, and description of a particular category from Youtube. The categories we can scrape are as:
- Science
- Food
- Travel
- Manufacturing etc.
Import Libraries
You need to import the necessary libraries like Pandas and Selenium.
from selenium import webdriver
import pandas as pd
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as ECSetting Up the Driver
You have to open Youtube in your browser. Type in the category you want to search videos for and set the filter to “videos.” You will get videos related to your search. Now, you have to copy the URL.
You need to set up the driver to fetch the content of the URL from Youtube.
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get("YOUR_LINK_HERE")Now, paste the link into driver.get(“YOUR_LINK_HERE”) function. Run the cell, and a new browser window will open for that link. You need to fetch the video links present on that particular page. You can create a list to store those links. Afterward, you must go to the browser window and do the following.
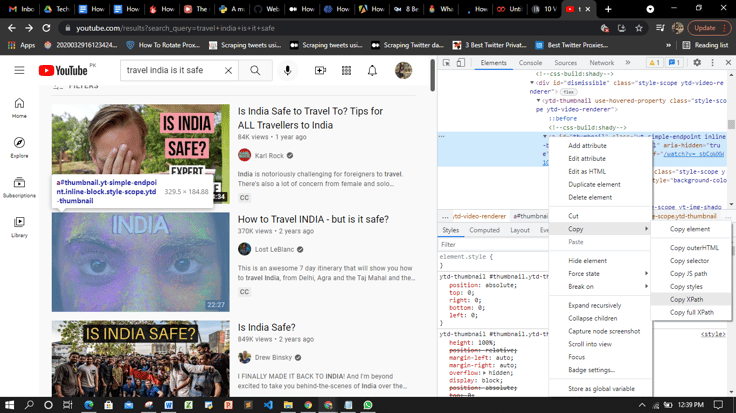
- Right-click on the page.
- Select the “Inspect” element.
You must search for the anchor tag with id = “video-title.” Right-click on it -> Copy -> XPath. The XPath will look something like this:
//*[@id=”video-title”]
Fetching the Youtube Video Links
You can use the below code to fetch the “href” attribute of the anchor tag you searched for.
user_data = driver.find_elements_by_xpath('//*[@id="video-title"]')
links = []
for i in user_data:
links.append(i.get_attribute('href'))
print(len(links))Create a DataFrame
You need to create a dataframe with the below four columns.
- link
- title
- description
- category
You can store the details of the videos for different categories in these columns.
df = pd.DataFrame(columns = ['link', 'title', 'description', 'category'])You are set to scrape the Youtube video details using Python’s below code.
wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10)
v_category = "CATEGORY_NAME"
for x in links:
driver.get(x)
v_id = x.strip('https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=')
v_title = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located(
(By.CSS_SELECTOR,"h1.title yt-formatted-string"))).text
v_description = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located(
(By.CSS_SELECTOR,"div#description
yt-formatted-string"))).text
df.loc[len(df)] = [v_id, v_title, v_description, v_category]Here,
- wait ignores instances of NotFoundException encountered by default in the “until” condition.
- The parameters ofthe wait function are: driver – It is the WebDriver instance to be passed to the expected conditions.timeOutInSeconds – It is the timeout when the expectation is called.
- driver – It is the WebDriver instance to be passed to the expected conditions.
- timeOutInSeconds – It is the timeout when the expectation is called.
- v_category is used for storing video category_name.
- We applied the for loop for the list of links created above.
- driver.get(x) performs the below functions: traverses through all the links one-by-oneopens them in the browser to fetch the details
- traverses through all the links one-by-one
- opens them in the browser to fetch the details
- v_id is used for storing the striped video ID from the link.
- v_title stores the video title fetched by using CSS_SELECTOR
- Likewise, v_description stores the video description by using CSS_SELECTOR
We will follow the same steps for the remaining categories. We will have four different dataframes, and we will merge them into a single dataframe. This way, our final dataframe will contain the desired details of the videos from all categories mentioned above.
frames = [df_travel, df_science, df_food, df_manufacturing]
df_copy = pd.concat(frames, axis=0, join='outer', join_axes=None, ignore_index=True, keys=None, levels=None, names=None, verify_integrity=False, copy=True)Using a Proxy to Scrape Youtube Videos
You can use Youtube proxies for the following tasks:
- Scraping – You can collect video titles, comments, and any information properly by using a proxy. You can also use a proxy to scrape Youtube videos that are within the Creative Commons domain. Therefore, you can add videos to your website without using Youtube as the official player.
- Unblocking Youtube – Many companies try to hide their content from the public for political or other reasons. With the help of the proxies, you can upload and watch Youtube content from a location where your access is restricted. Proxies help you access Youtube videos that your school or workplace has blocked.

Residential proxies are the best proxies for Youtube as compared to datacenter proxies. It is because the datacenter proxies get easily detected, and you have to face a lot of Captchas while using them. So, to avoid IP blocking and Captchas, residential proxies are best suited for Youtube automation.
Why Use Proxies For Scraping Youtube?
You know Youtube is filled with billions of pieces of valuable data. You can analyze this data and use it to do many things, such as:
- Making business decisions
- Marketing decisions
- Social research and studies
You need proxies when scraping Youtube. It is because Youtube employs advanced cybersecurity techniques that detect when you try to purchase multiple items from a single IP address. To circumvent detection, you must reroute your internet traffic through several proxy servers. This way, it will look like the network traffic is coming from different computers.
Proxies also act as a shield for marketers using Youtube bots to increase a video’s view count, manipulate the Youtube ranking algorithm, and claim revenue from ads.
Which Is the Best Proxy to Scrape YouTube Videos?
ProxyScrape is one of the most popular and reliable proxy providers online. Three proxy services include dedicated datacentre proxy servers, residential proxy servers, and premium proxy servers. So, what is the best proxy to scrape YouTube videos? Before answering that questions, it is best to see the features of each proxy server.
A dedicated datacenter proxy is best suited for high-speed online tasks, such as streaming large amounts of data (in terms of size) from various servers for analysis purposes. It is one of the main reasons organizations choose dedicated proxies for transmitting large amounts of data in a short amount of time.
A dedicated datacenter proxy has several features, such as unlimited bandwidth and concurrent connections, dedicated HTTP proxies for easy communication, and IP authentication for more security. With 99.9% uptime, you can rest assured that the dedicated datacenter will always work during any session. Last but not least, ProxyScrape provides excellent customer service and will help you to resolve your issue within 24-48 business hours.
Next is a residential proxy. Residential is a go-to proxy for every general consumer. The main reason is that the IP address of a residential proxy resembles the IP address provided by ISP. This means getting permission from the target server to access its data will be easier than usual.
The other feature of ProxyScrape’s residential proxy is a rotating feature. A rotating proxy helps you avoid a permanent ban on your account because your residential proxy dynamically changes your IP address, making it difficult for the target server to check whether you are using a proxy or not.
Apart from that, the other features of a residential proxy are: unlimited bandwidth, along with concurrent connection, dedicated HTTP/s proxies, proxies at any time session because of 7 million plus proxies in the proxy pool, username and password authentication for more security, and last but not least, the ability to change the country server. You can select your desired server by appending the country code to the username authentication.
The last one is the premium proxy. Premium proxies are the same as dedicated datacenter proxies. The functionality remains the same. The main difference is accessibility. In premium proxies, the proxy list (the list that contains proxies) is made available to every user on ProxyScrape’s network. That is why premium proxies cost less than dedicated datacenter proxies.
So, what is the best proxy to scrape YouTube videos?? The answer would be “residential proxy.” The reason is simple. As said above, the residential proxy is a rotating proxy, meaning that your IP address would be dynamically changed over a period of time which can be helpful to trick the server by sending a lot of requests within a small time frame without getting an IP block.
Next, the best thing would be to change the proxy server based on the country. You just have to append the country ISO_CODE at the end of the IP authentication or username and password authentication.
Suggested Reads:
Scrape YouTube Comments – 5 Simple StepsProxy For YouTube – 3 Important Types And Benefits
FAQs:
1. How To Scrape YouTube Videos Using Python?
2. Is it legal to scrape YouTube videos?
3. Is YouTube API available to normal users?
Final Thoughts on Scraping YouTube Videos Using Python:
For organizations and Youtube creators running their accounts, Youtube houses many useful data that can be scraped for analysis. Youtube scrapers extract data related to views, likes/dislikes, comments, and more, making it easier to make better business decisions. You can scrape Youtube videos using Selenium and Python and save a lot of time. The use of proxies is important because your account can get blocked if Youtube detects multiple requests from a single IP address. The best proxies for Youtube are residential proxies, as they are super fast and can not be detected easily.
I hope you got an understanding of how to scrape Youtube videos using Python.